Monday, May 19, 2008 - 1:30 PM
Medical Arts Building, Rm M-143 (Queensborough Community College)
243
Electric Field Responsive Ionic Liquid Polymers
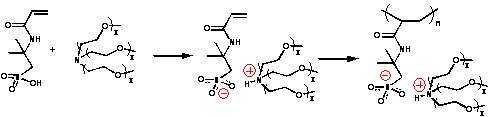
Abstract: The electrowetting behavior of ionic liquids as well as electrolyte solutions can manifest itself in a shape change of a droplet on a surface or translational movement across that surface. The magnitude of the response depends on the strength of the electric field, the nature of the surface being wetted (surface energy, roughness) by the droplet and on the chemical nature of the ionic liquid itself (composition, structure, conductivity, surface tension, viscosity). In the work to be presented we focus on an ionic liquid monomer – liquid polymer system based on an acrylamidopropane sulfonic acid – oxyethylene amine base (depicted below) and describe comparative electrowetting measurements. The contact angle dependence on electric field and polarity as well as translational droplet motion will be illustrated. The issues of interest are comparison of a monoionic with a polyionic liquid system, the molecular weight effect of polyionic system and volume fraction effect of the oxyethylene ammonium counter ion.